20
age unchanged, given that the individual had a full record of 30 years of service.
Therefore the long-run effects on income are negligible. All things considered, we
conclude that the potential income effects on health are small.
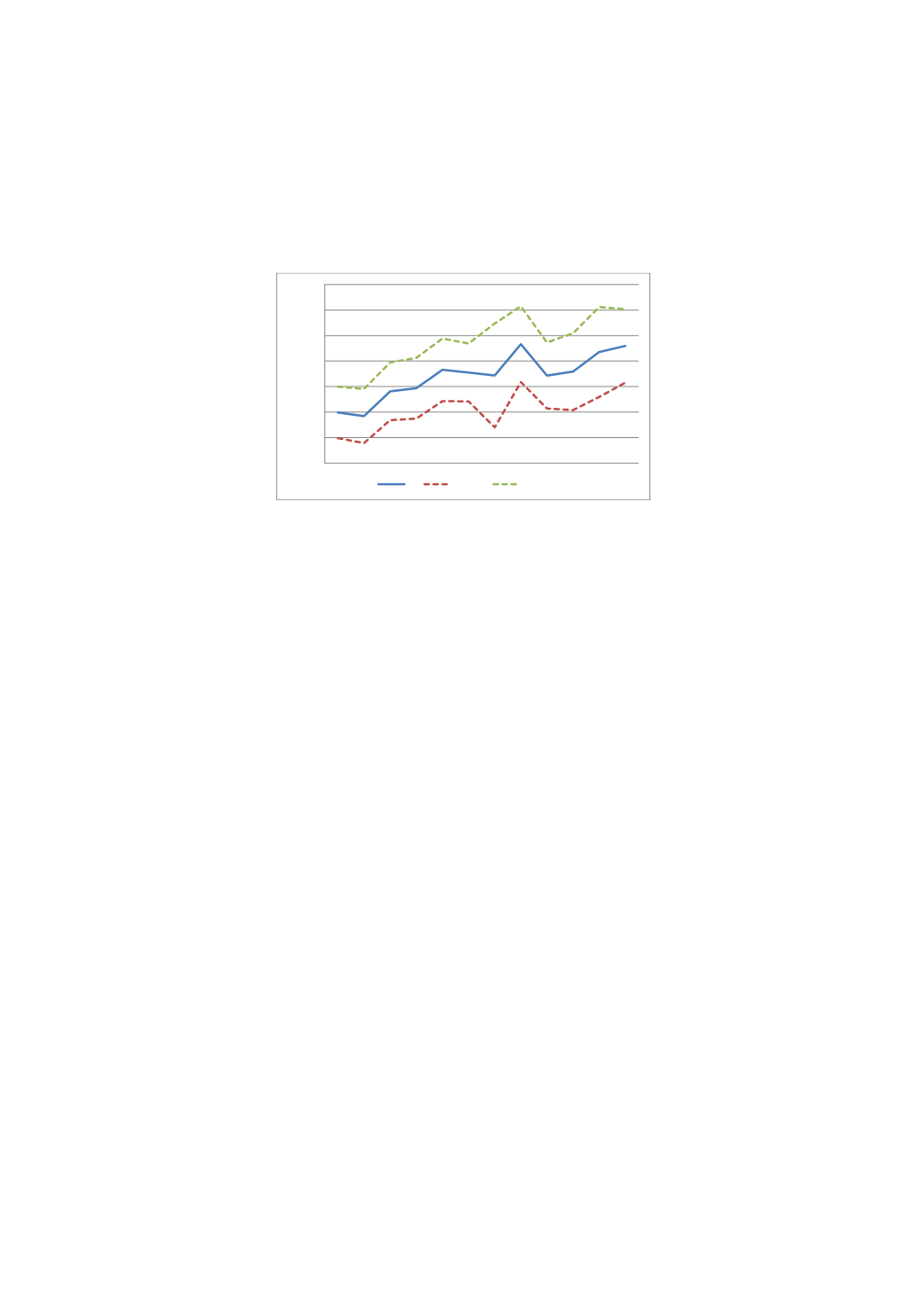
Figure 8: The effect on disposable income (SEK per year); the interaction term in a difference-
in-difference specification; other variables include dummy for military and birth year 1938-1939
6.2
The effect on inpatient care
The analysis of the effects on the number of days in inpatient care is based on the log
linear specification shown in (4). The parameters are estimated using a pseudo-
maximum-likelihood estimator (using the Poisson distribution in the maximization).
The standard errors are estimated using the robust covariance matrix (or the sandwich
estimator) and are hence robust to overdispersion. The geographic location of military
employees differs from that of other government employees. As there could potentially
be different business cycles across regions and regional differences in health care which
both could affect health we control for the residential county of the employees when
they are 54 years old. In addition we control for labor income at age 54 and education
level in a separate regression.
The result from the estimation is displayed in
The results without controls
are provided in columns (1), (3) and (5), while columns (2), (4) and (6) provide results
when we add control variables. The results when estimating the effects over the age
span 56-70 are presented in columns (1) and (2). In order to study if the effect stems
mainly from the first 5 years (when the comparison group is mainly working) or if the
effect is more long lasting, we also present results in columns (3)-(6) where the number
of days in inpatient care is measured at ages 56-60 and 61-70, respectively.
We find that the number of days in inpatient care for ages 56-70 is reduced by
approximately 35 percent on average, due to the opportunity for early retirement.
-40 000
-30 000
-20 000
-10 000
0
10 000
20 000
30 000
59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70
b
b-2*se
b+2*se


