27(40)
Figur 2.
Policy simulation: Tooth extraction vs. Full examination,
performed by dental hygienist.
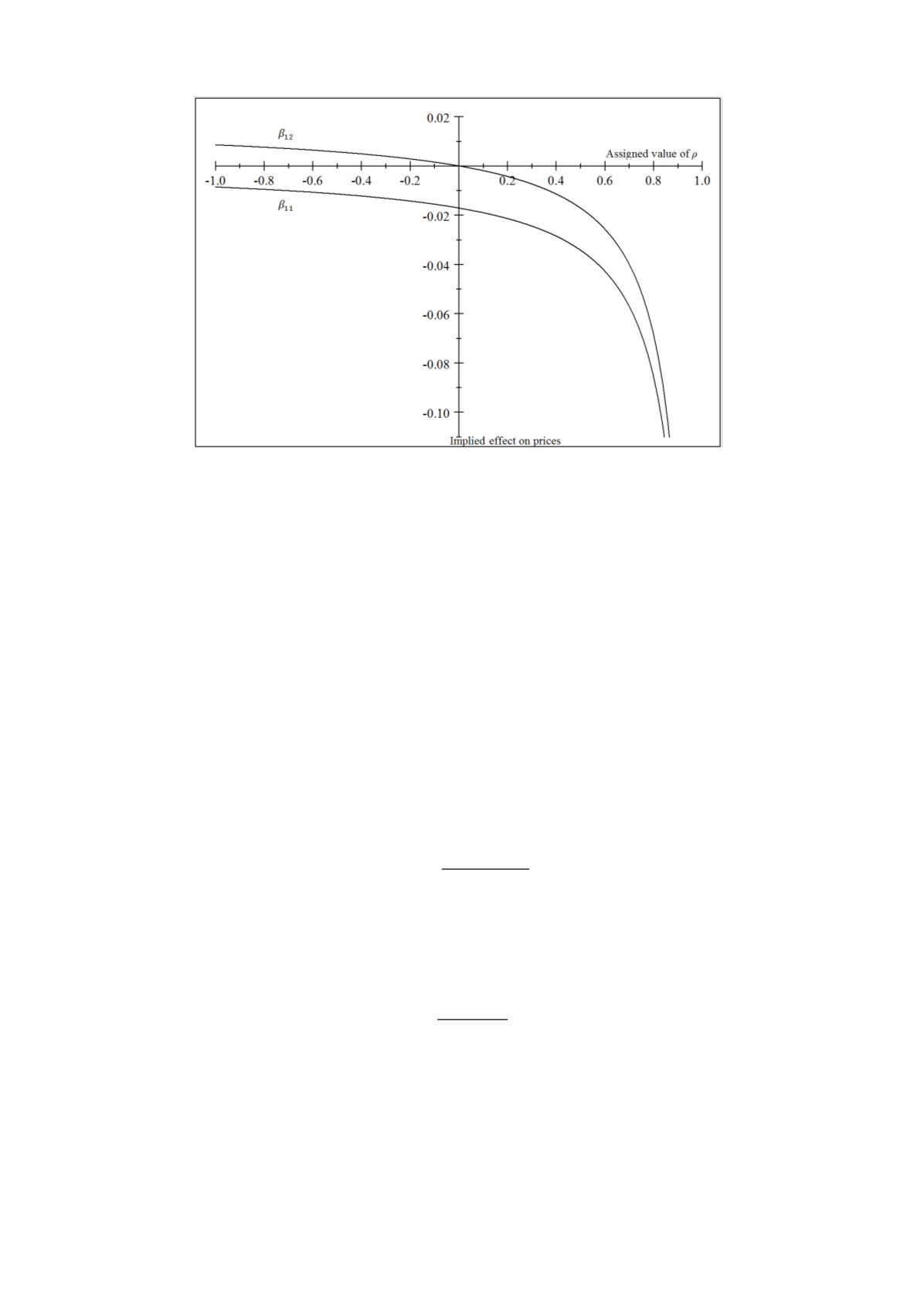
It is clear that the welfare implications for consumers differ depending
on where we are on the abscissa, i.e. the value of
. If
is positive,
competition has negative effects on prices for both types of services.
Therefore,
can be thought of as a measure of the overall competitiveness
of the market.
In order to say something about welfare implications, I need to assess
the value of
. An estimate of
should reflect overall competitiveness and
from (7) we have that
captures how
and
are related. A natural
measure of competitiveness is firms’ market power, defined as their ability
to set prices above costs (Corts, 1999). I therefore define
as the average
markup for first-stage services relative to the average markup for follow-on
services. Mark-ups are defined by relating treatment prices to their
respective reference price (described in section 4). Using reference prices
as a proxy for marginal costs, I get an estimate of the mark-up in the
following way:
is the average price for treatment
at clinic
in year
and
is the
average reference price for treatment
in year
. On average, the mark-up
is higher for tooth extractions compared to examinations, implying a lower
mark-up for the latter. Finally, I define
in the following way:
(8)
Where
is the average markup for examinations and
is the average
markup for tooth extractions.
can be smaller than zero and larger than
one, as clinics may set prices below and well above the reference price.


